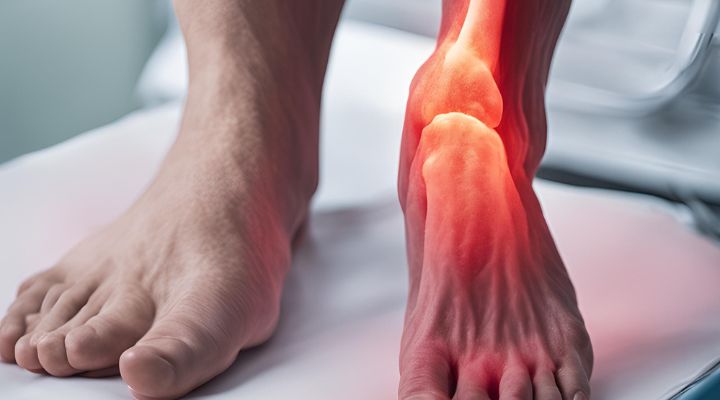
Ankle swelling, also known as edema, can be a cause of concern for many individuals. It is often a sign of underlying health issues or temporary conditions that cause fluid accumulation in the tissues surrounding the ankle joint. Understanding the causes of ankle swelling can help prevent or address the problem. Below, we explore five common reasons behind swollen ankles and how to manage them effectively.
1. Injury or Trauma to the Ankle
Injuries such as sprains, fractures, and strains are among the most frequent causes of ankle swelling. When you injure your ankle, the body’s natural response is to send fluids and white blood cells to the affected area to promote healing. This causes the tissues around the ankle to become inflamed and swollen.
Symptoms of Injury-Related Ankle Swelling:
- Immediate pain following a twist, fall, or blow to the ankle.
- Bruising and tenderness around the affected area.
- Difficulty walking or standing.
- Swelling that appears quickly after the injury.
How to Manage Injury-Related Ankle Swelling:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured ankle.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to wrap the ankle and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the ankle elevated above heart level to minimize fluid buildup.
- Consult with a healthcare professional if the pain persists or worsens.
2. Poor Circulation and Venous Insufficiency
One of the leading causes of chronic ankle swelling is poor circulation, particularly a condition called venous insufficiency. In this condition, the veins in your legs struggle to send blood back to the heart, leading to a buildup of fluid in the tissues of the lower extremities, including the ankles.
Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency:
- Swelling in both ankles, which may worsen after standing for long periods.
- Skin discoloration around the ankles or legs.
- A feeling of heaviness or tiredness in the legs.
- Varicose veins or visible vein patterns.
How to Manage Venous Insufficiency:
- Exercise regularly to improve blood circulation in the legs.
- Wear compression stockings to encourage better blood flow.
- Elevate the legs when sitting or lying down to reduce swelling.
- Avoid prolonged standing or sitting for extended periods.
- Consult a healthcare provider about medications or procedures if necessary.
3. Heart, Kidney, or Liver Conditions
Systemic health problems, particularly those related to the heart, kidneys, or liver, can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the ankles and other areas of the body. In these cases, ankle swelling is often a sign of a more serious underlying issue.
Heart Failure and Ankle Swelling:
- When the heart cannot pump blood effectively, fluid can accumulate in the legs and ankles, causing swelling.
- Congestive heart failure often results in swelling in both ankles, along with symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and rapid weight gain.
Kidney Disease and Ankle Swelling:
- The kidneys play a vital role in removing excess fluids from the body. If they are not functioning properly, fluid retention can occur, causing swelling in the lower extremities.
Liver Disease and Ankle Swelling:
- Conditions like cirrhosis can affect the liver’s ability to regulate fluid levels, leading to edema in the ankles and abdomen.
How to Manage Swelling from Heart, Kidney, or Liver Issues:
- Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Follow a low-sodium diet to prevent excessive fluid retention.
- Take prescribed medications that help remove excess fluids from the body.
- Monitor weight and swelling regularly to detect any changes in condition.
4. Pregnancy
During pregnancy, many women experience swollen ankles, particularly in the later stages. Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins in the pelvis can slow down blood circulation, leading to fluid buildup in the ankles.
Symptoms of Pregnancy-Related Ankle Swelling:
- Swelling in the ankles and feet, especially later in the day or after prolonged standing.
- Mild discomfort or tightness in the swollen areas.
- Swelling that becomes more noticeable as pregnancy progresses.
How to Manage Pregnancy-Related Ankle Swelling:
- Elevate the feet whenever possible.
- Avoid standing for long periods and take regular breaks to walk around.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and reduce fluid retention.
- Wear comfortable shoes with proper support to avoid additional strain on the ankles.
- If the swelling is severe or accompanied by other symptoms such as headaches or vision changes, consult a healthcare provider to rule out conditions like preeclampsia.
5. Prolonged Sitting or Standing
Extended periods of sitting or standing can cause gravity-induced swelling in the ankles. This is especially common for individuals who travel frequently or work in professions that require long hours of standing. When you remain in one position for too long, blood pools in the lower extremities, leading to fluid buildup and swelling.
Symptoms of Swelling Due to Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
- Gradual swelling in the ankles and feet as the day progresses.
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the lower legs.
- Swelling that improves with movement or after a period of rest.
How to Manage Swelling from Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
- Move regularly to stimulate circulation, such as walking or doing calf stretches.
- Wear compression socks if your job requires long periods of standing.
- Elevate your feet when resting to reduce fluid accumulation.
- Avoid sitting with your legs crossed, as this can impede circulation.
Swollen ankles are often a symptom of underlying issues that range from mild to serious. Whether caused by an injury, circulation problems, pregnancy, or health conditions like heart or kidney disease, understanding the root cause is essential for proper treatment. If you experience persistent or unexplained swelling, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of action.