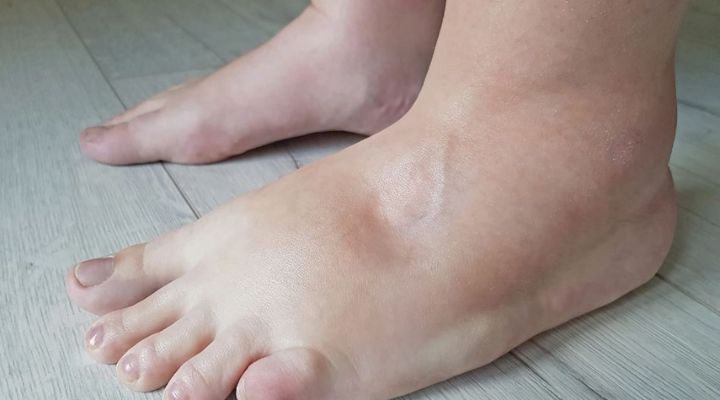
Introduction
Water retention, also known as edema, occurs when excess fluids build up inside your body. It can cause swelling in various parts of the body, including the legs, feet, ankles, and hands. Understanding the causes of water retention is crucial because it can affect your health and daily comfort. Let’s dive into the six main causes of water retention and explore effective ways to reverse it.
Cause 1: High Sodium Intake
Sodium is an essential mineral that helps maintain fluid balance in your body.However, excessive sodium intake can cause water retention. When you eat a lot of salty foods, your body holds onto extra water to dilute the excess sodium, leading to swelling and bloating. This is why reducing your sodium intake is a key step in managing water retention.
Cause 2: Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can cause water retention. Many women experience bloating and swelling during their menstrual cycle due to hormonal changes. Additionally, hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can also lead to water retention. Understanding these hormonal triggers can help in managing the symptoms.